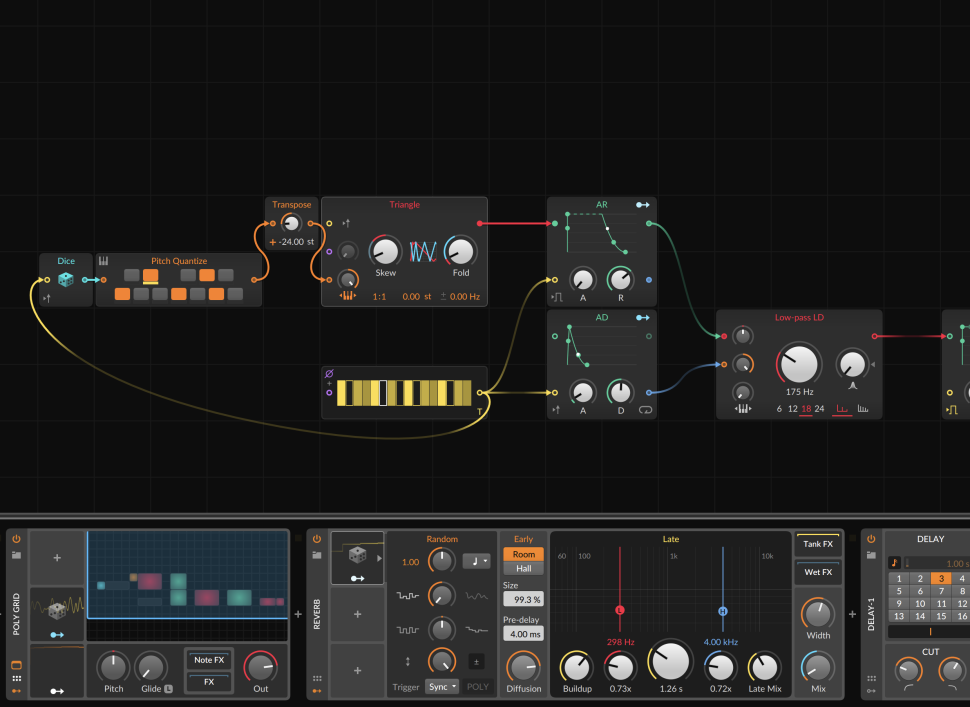
1 Poly grid
As a basis for the project we use - of course - an instance of Poly Grid and place an ADSR module there directly between Triangle and Mixer. Turn Sustain all the way up, so that the output is only heard when you play a note; otherwise, the sound runs through permanently. A Dice module should serve as the basis for sequences and melodies
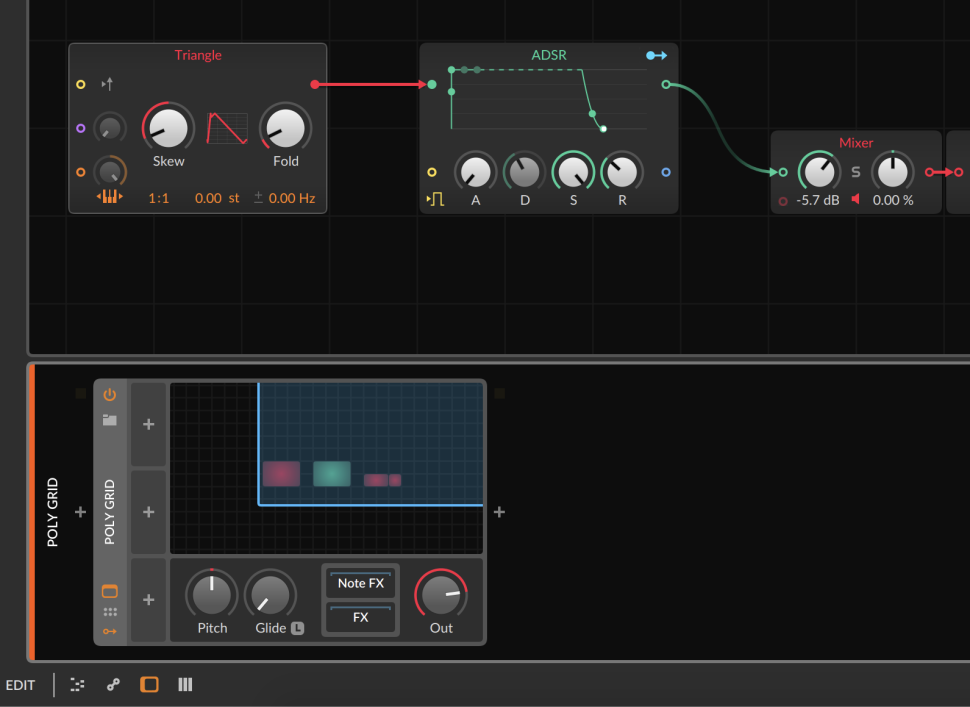
2 Quantize chance
To make sure that the results are not completely arbitrary, we add a Pitch Quantize and a Transpose module that feeds into Triangle‘s PITCH IN. We turn up the modulation control to full. Using Transpose, we pitch the notes down 24 semitones. This can also be done directly in the Triangle module, but we will need the extra module later
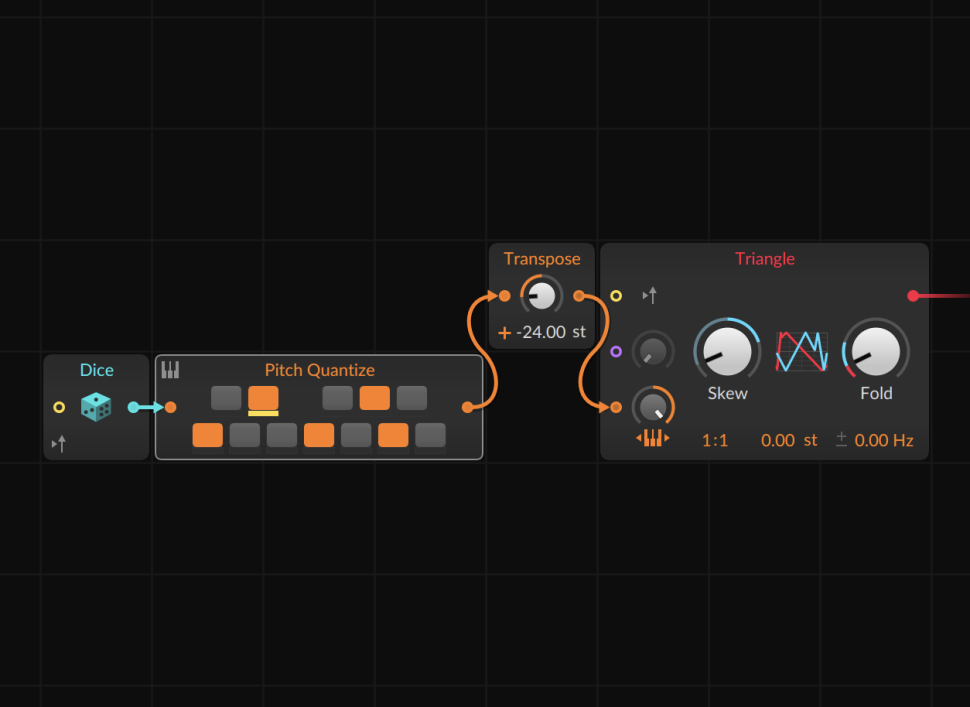
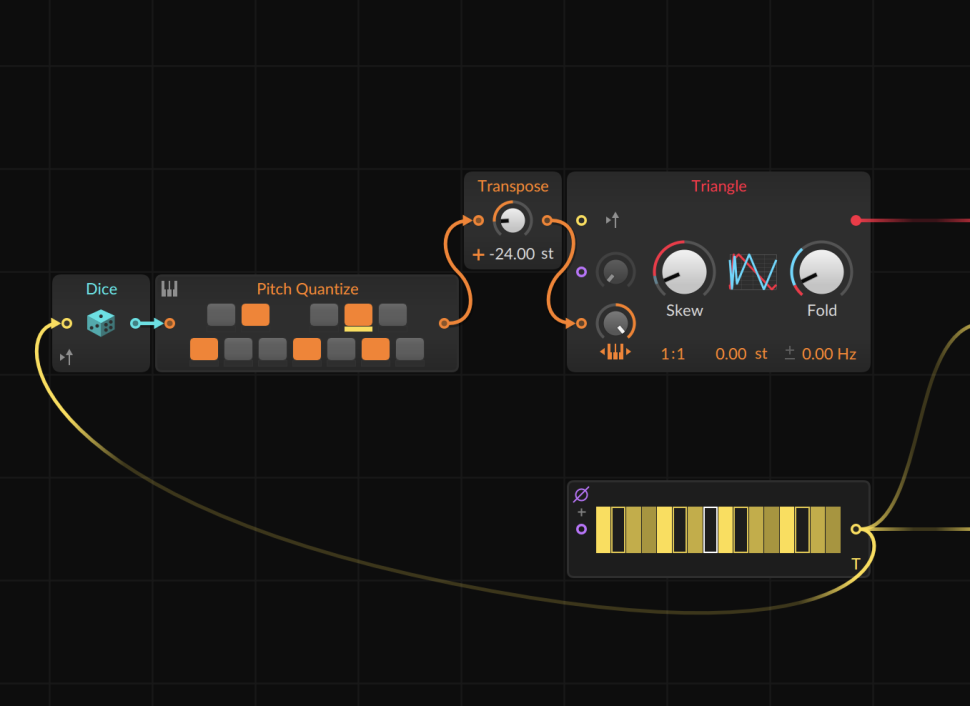
3 Set scales
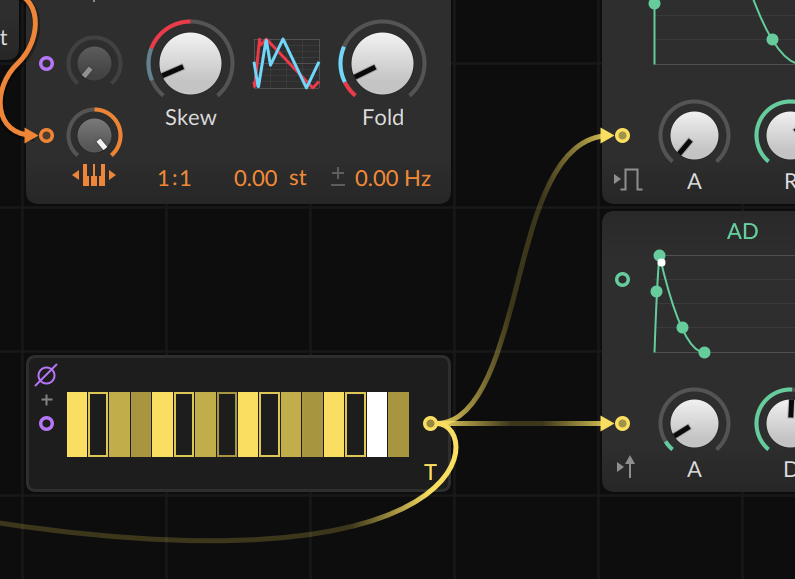
In Pitch Quantize, we program an arbitrary scale within which the notes are to fall. In order for the previous construct to generate an output, we still need a trigger. For this, we use a Gates module. We set its step count to 16 and activate some of the steps. We route the output to the Trigger In of Dice.
4 Add a filter
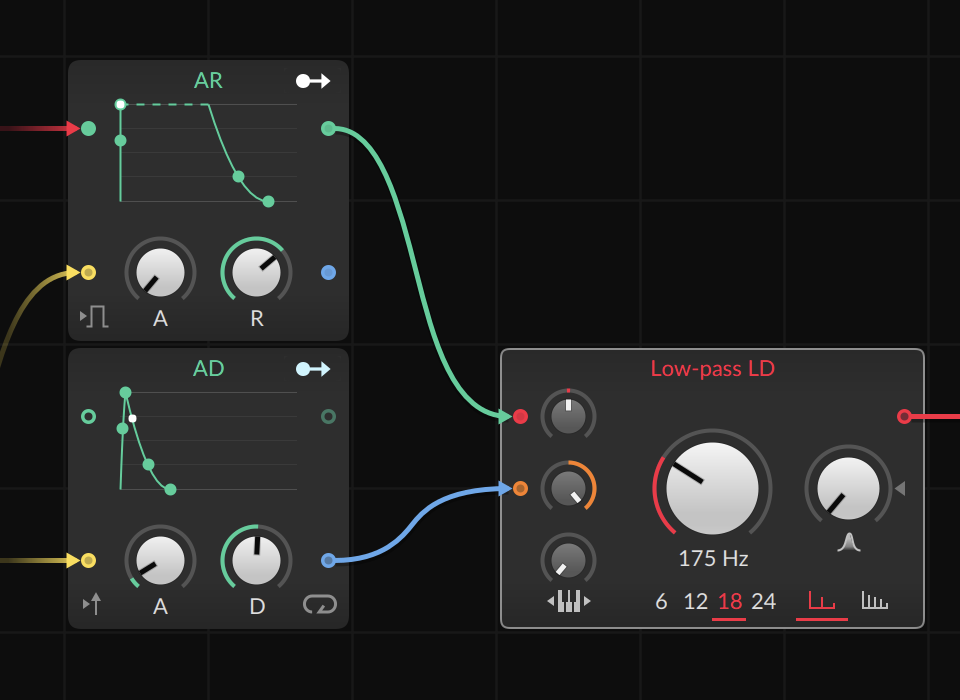
We make the sound a bit more pleasant: we route Triangle into an AR envelope which, in turn, goes into the Low Pass LD Filter and finally moves into the first ADSR envelope. To do this, we connect an AD envelope to the filter‘s CUTOFF IN and turn the modulation all the way up, and CUTOFF all the way down. A clear plus for the sound
5 More gates
The new envelopes are also triggered by the Gates module. Important: TRIGGER and GATE IN must be deactivated for both of them (with the icons on the bottom left of the modules); otherwise, they will only react to incoming notes and not to the sequence of the Gates module. To make the sound nicer, we load a REVERB and DELAY behind the POLY GRID
6 Effects
With the POLY GRID, we open the MODULATORS, load Random (LFO) and connect it to the Skew parameter in the Triangle module. With the REVERB, we also load a random modulator and let it process the Mix knob. This gives us a great basis for generative sounds that can be extended in many directions